Data Center Cooling
The data center is a crucial component of the information industry, but as high-density, high-power servers become more prevalent, the energy consumption of these centers has risen dramatically. It has been reported that the data center cooling system accounts for approximately 40% of a data center’s energy usage.
In order to meet the cooling requirements of the equipment room while reducing the energy consumption of the cooling system, natural cooling technology is becoming increasingly recognized as an effective means of enhancing energy efficiency. The use of data center heat exchanger is one such technology that is gaining momentum in the effort to improve the cooling efficiency of data centers.
Raised Floor Systems and Data Center Cooling: A Traditional Approach to Server Cooling
For many years, raised floor systems have been employed in computer rooms and data centers to provide cooling to servers. These systems use a computer room air conditioner (CRAC) or computer room air handler (CRAH) to supply cold air, which pressurizes the area underneath the raised floor. The cold air is then released into the main space through perforated tiles, with the aim of entering server intakes. The heated air from the servers then returns to the CRAC/CRAH to be cooled, typically after mixing with the cold air.
The CRAC unit’s return temperature is often used as the set point for controlling the cooling system’s operation. In most cases, the CRAC unit’s fans run at a constant speed, and a humidifier within the unit generates steam. The incorporation of data center cooling systems such as CRAC and CRAH, along with raised floor systems, has been a common approach to maintaining the ideal operating conditions for servers.
The traditional system used in data center cooling is based on the principle of comfort cooling, which involves providing a relatively small quantity of conditioned air that mixes with the larger volume of air in the space to achieve the desired temperature. This method was effective when information technology equipment (ITE) densities were low, allowing the system to meet its primary objective despite its inefficiencies, uneven cooling, and other drawbacks.
While raised floor systems with air delivery are still utilized in some data centers, their prevalence has decreased as advancements in air delivery techniques have made them redundant. This does not necessarily imply that raised floor systems are obsolete, as some companies still rely on them for data center cooling.
What is Natural Data Center Cooling?
Natural cooling of data centers is an eco-friendly and cost-effective alternative to traditional cooling methods that utilize mechanical equipment, such as air conditioners and chillers. Natural cooling involves the use of ambient air temperature and outside air to regulate the temperature of the data center, rather than relying solely on mechanical cooling equipment.
One approach to natural cooling is to use outdoor air directly, which is drawn into the data center through vents or other openings. The air is then filtered, and any contaminants or impurities are removed before it is used to cool the equipment. This method is particularly effective in areas with cooler climates or during periods when the outside temperature is lower, such as during the night.
Another approach is to use indirect air-side economization, which involves using heat exchangers to transfer heat from the data center’s exhaust air to the cooling water. This method allows for greater control of the temperature within the data center.
Natural cooling methods can significantly reduce the energy consumption and carbon footprint of a data center.
Categories of Natural Data Center Cooling?
Natural cooling is mainly divided into two categories: windside natural cooling and waterside natural cooling.
Windside natural cooling
Direct type: Utilizes the wind to cool the data center. Air is drawn into the data center through vents or other openings and circulated through the space to cool the equipment.
Indirect type: indirect outdoor cold air into the room, through heat exchanger (dry/wet), heat pipe, and recycle refrigerant.
Waterside natural cooling
Direct type: Direct uses a water source, such as a river or lake, to cool the data center. Water is pumped from the source through a heat exchanger to transfer heat from the data center’s cooling system to the water. The heated water is then discharged back into the water source.
Indirect type: Cooling tower cooling water direct cooling, cooling tower + plate heat exchanger, closed cooling tower, dry cooler.
Unsure about which Plate Heat Exchanger to utilize?
Contact us for 1-on-1 Expert guidance and custom design services tailored specifically to your needs!
Optimizing Data Center Cooling Efficiency: Hybrid Approach Using Chiller and Natural Cooling Technologies
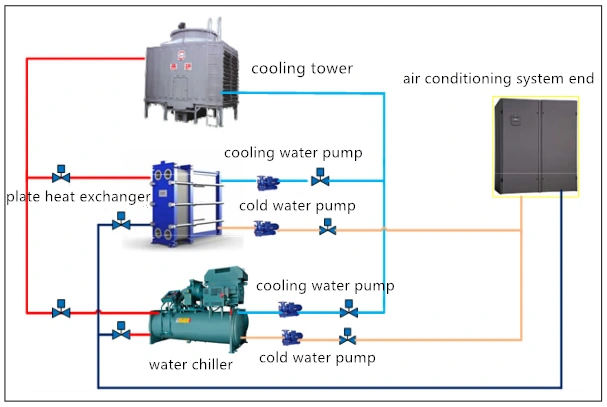
Natural cooling technology is a method of using natural cold sources to reduce the reliance on chillers and other mechanical refrigeration systems in data center cooling, resulting in decreased energy consumption. To achieve this, water-water plate heat exchangers and related equipment are added to the conventional air-conditioning water system.
The plate heat exchanger operates in parallel with the chiller, both of which have their independent cooling water pumps and chilled water pumps. The chilled water is circulated through a cooling tower, a cooling water pump, and the plate heat exchanger, which exchange heat and reduce the temperature of the machine room. When the chilled water supply temperature meets the required level, the plate heat exchanger replaces the chiller, achieving natural cooling. However, if the temperature of the cooling water cannot cool the chilled water to the desired temperature, the chiller is used for direct cooling.
Cooling Tower Natural Data Center Cooling
Data center cooling has traditionally relied on mechanical cooling methods that consume significant amounts of energy. However, natural cooling technologies are gaining traction as a more energy-efficient and cost-effective alternative. Among these natural cooling methods, cooling tower type natural cooling stands out as one of the most widely used in data centers.
Cooling tower natural cooling technology utilizes lower outdoor air temperatures to produce cold water through a cooling tower. This cold water can be used to replace mechanical cooling and provide cooling for the data center. There are several types of cooling tower natural cooling, including:
1. Open cooling tower direct natural cooling, where the cold water produced by the cooling tower is directly used in the precision air conditioner of the machine room.
2. Open cooling tower indirect natural cooling, where the cold water prepared by the cooling tower exchanges heat with the high-temperature backwater of the precision air conditioner in the machine room through the plate heat exchanger, achieving cooling for the machine room.
3. Closed cooling tower natural cooling, which uses a closed cooling tower or low-temperature ethylene glycol solution to produce low-temperature water for direct use in the precision air conditioning system of the machine room.
4. Dry cooler natural cooling, which utilizes a tubular heat exchanger placed in the tower. The circulating water or ethylene glycol solution from the precision air conditioner of the machine room is cooled by the low-temperature cold air circulating through the outside.
By using natural cooling technologies like cooling tower natural cooling, data centers can significantly reduce their energy consumption and environmental impact while still achieving the necessary cooling for their equipment.


Advantage and Disadvantage of Cooling Tower Data Center Cooling
Cooling towers are often used in data centers to remove heat from the equipment and maintain a stable operating temperature. Here are some advantages and disadvantages of using a cooling tower in a data center:
Advantages:
1. Energy-efficient: They use less energy compared to other cooling systems since they rely on natural air movement rather than electricity to remove heat from the water.
2. Cost-effective: Cooling towers are generally cheaper to install and maintain than other cooling systems, such as chillers or air conditioning units.
Disadvantages:
1. Weather dependency: Cooling towers rely on outdoor air temperature and humidity levels. In hot and humid climates, cooling towers may not be able to provide enough cooling, which can cause equipment to overheat. Besides, in cold regions, the antifreeze problem of open cooling towers is critical and should be taken seriously.
Plate Heat Exchanger in Data Center
The computer equipment room maintains a consistent temperature and humidity level year-round. Specifically, the temperature within the room is kept between 18-24 degrees Celsius. To accomplish this, plate heat exchangers are utilized to cool the equipment room’s cooling water with either pure water or water containing ethylene glycol.
It’s worth noting that the effectiveness of the plate heat exchangers is dependent on the temperature differential between the two sides of the exchanger, which ranges between 1-1.5°C. As an example, the supply/return water temperature on one side measures 13.5-13.5/18.5°C while the other side measures 21/15°C. Moreover, the pressure drop experienced by the system is less than or equal to 50kPa.
