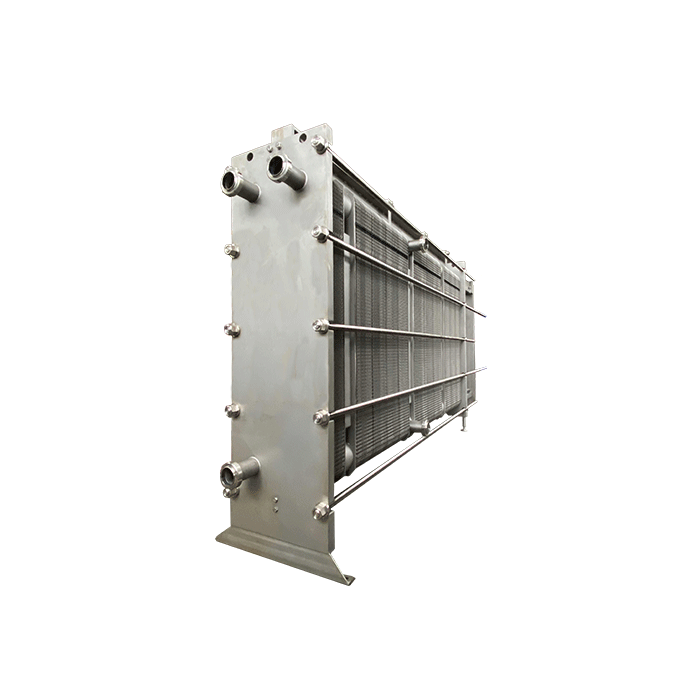
1. HFM Plate Heat Exchanger for Wineries
Plate heat exchangers have become integral in modern winemaking, ensuring precise temperature control throughout the production process. At HFM, we take pride in offering advanced plate heat exchanger solutions tailored to the unique demands of the wine industry.
With a focus on efficiency and quality, our plate heat exchangers have found widespread application in fermentation, clarification, and stabilization processes. Experience the seamless integration of technology and tradition in the pursuit of the perfect bottle. Contact Us or send us an email at: [email protected] to learn more.
2. The Role of Plate Heat Exchangers in Wine Production
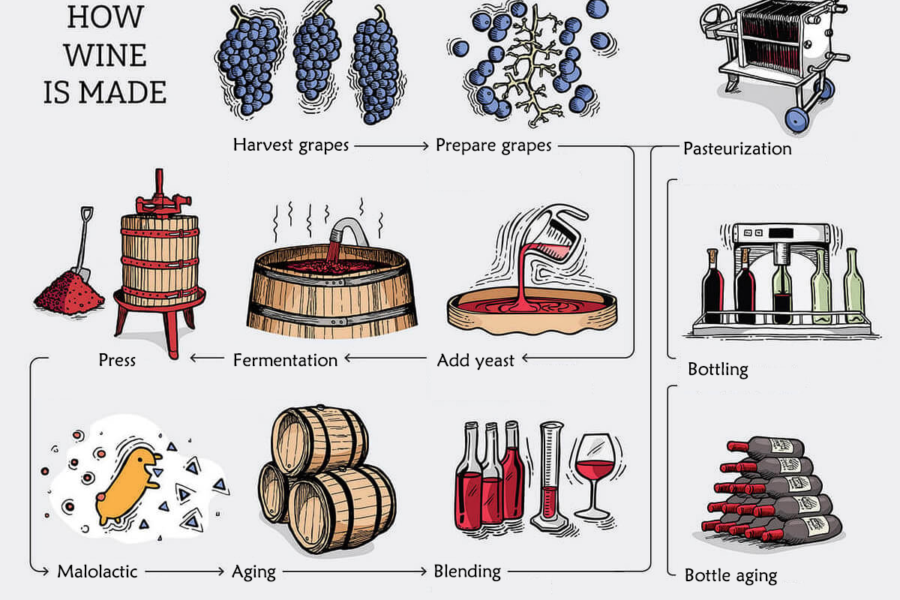
Plate heat exchangers stand as indispensable tools in the enhancement of every crucial stage in wine production. Specifically engineered for this purpose, these heat exchangers excel in maintaining exacting temperature levels. This precision in temperature regulation is paramount in guaranteeing that the resulting wine attains the pinnacle of quality, characterized by its distinct flavor profile, aroma, and overall excellence.
1. Harvesting:
Grape harvesting is a pivotal stage in winemaking. The timing of the harvest is determined by factors such as sugar content (measured in Brix), acidity, and flavor development.
2. Prepare Grapes:
Following harvest, the grapes undergo meticulous preparation. They are transported to the winery in bins or crates, where any undesirable grapes, leaves, or debris are removed during this process.
3. Add Yeast:
In this step, the winemaker introduces yeast into the grape must. This inoculation is a critical step as yeast is responsible for the fermentation process. Winemakers can use natural yeast present in the vineyard or employing specific cultured strains. This choice has a significant impact on the wine’s final flavor and aroma profile.
4. Fermentation (Involving Heat Exchangers):
Plate heat exchangers play a critical role in the fermentation process. During this stage, grape juice is transformed into wine through the action of yeast. The heat exchanger maintains the ideal temperature, ensuring producing wine with the desired flavor profile and alcohol content.
5. Pressing:
After fermentation, the wine undergoes a pressing process. This separates the liquid wine from the solid grape matter (skins, seeds, and sometimes stems). Pressing process extracts color, flavor, and tannins from the grape skins. For white wines, pressing is typically gentler to avoid excessive extraction.
6. Clarification and Filtration (Involving Heat Exchangers):
Achieving clarity in wine is paramount. Plate heat exchangers aid in effectively removing unwanted particles and impurities. By utilizing heat exchangers, winemakers ensure that the wine is visually appealing and free from any undesirable elements that may affect taste or appearance.
7. Stabilization (Involving Heat Exchangers):
The stabilization of wine involves adjustments to its chemical composition, ensuring it remains consistent and maintains quality over time. Plate heat exchangers play a vital role in this process by providing precise temperature control. This is crucial in maintaining desired chemical balance and preventing any unwanted reactions that might occur with temperature fluctuations.
8. Malolactic Fermentation:
In certain cases, winemakers opt for a secondary fermentation known as malolactic fermentation. This process involves converting tart malic acid into milder lactic acid, resulting in a smoother, softer wine. It can contribute to a rounder mouthfeel and alter the wine’s flavor profile.
9. Aging:
Aging is the process of allowing the wine to develop and mature in barrels or tanks. This step contributes to the wine’s complexity and smoothness, and is typically done in controlled environments.
10. Blending:
Winemakers may mix different batches or varieties of wine to achieve specific flavor profiles and balance. This step allows for creativity and consistency for the final product.
11. Pasteurization (Involving Heat Exchangers):
Pasteurization is pivotal for wine safety, using controlled heat to eradicate harmful microorganisms. Plate heat exchangers guarantee exact temperature control in this critical process. This ensures product safety and stability, deactivates enzymes for flavor preservation, prevents unwanted fermentation, maintains desired characteristics, and ensures regulatory compliance.
12. Bottling:
This step involves filling bottles, sealing, and labeling them for distribution. It’s a critical stage in preparing the wine for market.
13. Aging in Bottle:
Some wines benefit from additional aging in the bottle, allowing further development of aroma and flavor.
14. Quality Control and Testing (Involving Heat Exchangers):
Plate heat exchangers are instrumental in quality control processes. They contribute to ensuring that the wine meets industry standards and specifications. Through precise temperature management, heat exchangers assist in conducting rigorous testing to guarantee that the final product is of the highest quality.
By integrating plate heat exchangers into these critical stages of wine production, winemakers can exert greater control over the process, resulting in wines of superior quality and consistency.
3. Key Advantages of Plate Heat Exchangers in Wine Production
1. Efficient Heat Transfer:
Plate heat exchangers employ a sophisticated design that facilitates a remarkably efficient exchange of thermal energy. This means that they can rapidly heat or cool wine to the desired temperature, a critical factor in achieving consistent and high-quality wine production. By swiftly adjusting temperatures, winemakers can optimize various stages of the production process, such as fermentation and stabilization, leading to wines with precise flavor profiles and characteristics.
2. Space Efficiency:
One of the standout features of plate heat exchangers is their compact footprint. Unlike some other types of heat exchangers, which can be bulkier, plate heat exchangers are specifically engineered to maximize space utilization in production facilities. Their streamlined design allows for efficient placement within existing setups, ensuring that valuable space is not unnecessarily occupied. This space-saving characteristic is particularly advantageous for wineries with limited square footage.
3. Customization:
Plate heat exchangers are highly adaptable and can be tailored to meet the specific operational needs of a winery. This customization capability allows for seamless integration into existing production systems. Factors such as flow rates, temperature differentials, and other critical parameters can be precisely calibrated to align with the unique requirements of the wine production process. This level of adaptability ensures that the plate heat exchanger becomes an integral and optimized component of the overall production setup.
4. Easy Maintenance:
Accessibility is a paramount consideration in the design of plate heat exchangers. This accessibility translates to ease of maintenance, a crucial factor in ensuring uninterrupted and efficient production. Winemakers can readily access and clean the plates, preventing the buildup of impurities or fouling that can diminish performance. The simplicity of maintenance tasks means that downtime is minimized, allowing for consistent and reliable operation.
5. Energy Efficiency:
Plate heat exchangers are engineered to provide precise temperature control. This level of control translates to energy efficiency, as it minimizes the amount of energy required to achieve and maintain the desired temperatures. By reducing energy consumption, wineries can not only lower operational costs but also contribute to sustainability efforts. This aligns with an industry-wide trend towards adopting environmentally-conscious practices, making plate heat exchangers a favorable choice for eco-conscious winemakers.
4. Example of Grapes for Wine Production
| White grape | Riesling | Rkatsiteli | Italian Riesling | Pinot Blanc | Chardonnay | Sauvignon Blanc | Chenin Blanc | Semillon | Pinot Gris |
| Red grapes | Carignan | Cabernet Sauvignon | Cabernet Gernischt | Cabernet Franc | Pinot Noir | Merlot | Syrah/Shiraz | Barbera | Malbec |
5. Plate Heat Exchanger Solution
1. Sterilization process
Hot side: water or steam inlet temperature 100 to above
Cold side: wine outlet temperature is about 90-95
Plate material: 316/304(1.4308,1.4408 of German / European standard)
Gasket: EPDM
2. Filling process
Hot side: wine, imported 90-95 outlet about 80 degrees
Cold side: water, normal temperature water
Board material: 316/304(1.4308,1.4408 of German / European standard)
Gasket: EPDM
6. Products